As math enthusiasts, we know that angles are an important concept in geometry. But do we really understand what an angle is and how to measure it?
An angle is formed when two lines intersect each other at a common point. This point is called the vertex of the angle. The two lines that form the angle are called the arms or sides. The measure of an angle is the amount of rotation needed to bring one arm of the angle to coincide with the other arm.
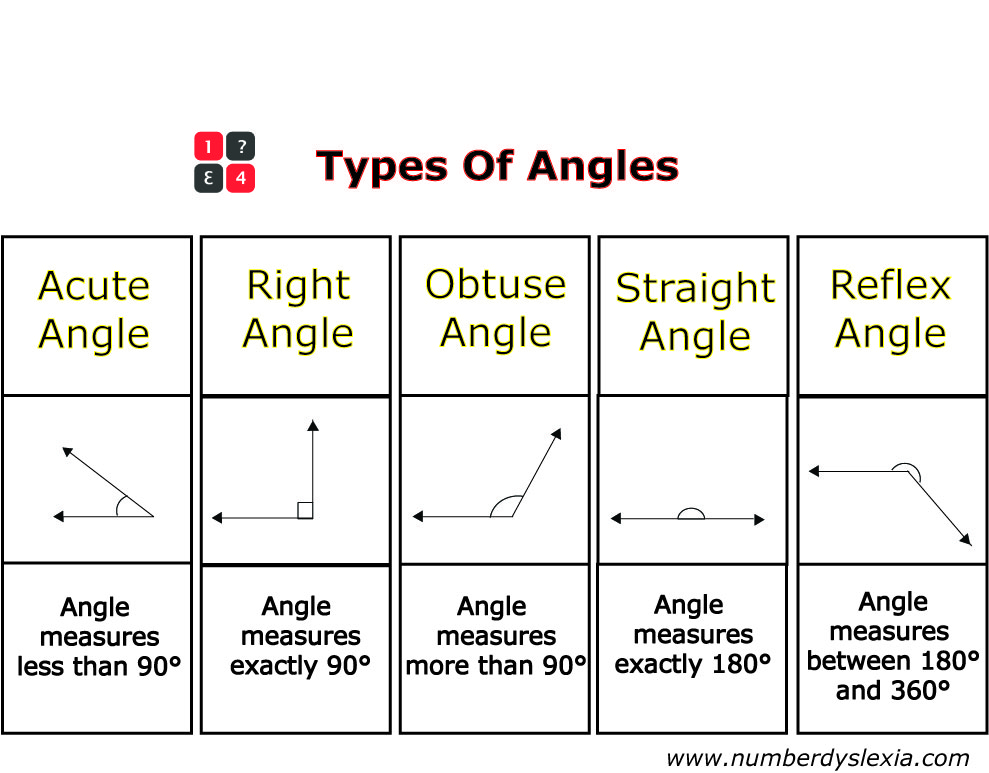
Angles are measured in degrees, which is denoted by the symbol °. A full rotation around a point is equal to 360°. Therefore, we can say that a straight angle, which is formed by two opposite rays and measures 180°, is half of a full rotation. A right angle, which is formed by a horizontal line and a vertical line and measures 90°, is one-quarter of a full rotation.
We can classify angles based on their measures. Angles that measure less than 90° are called acute angles. Angles that measure exactly 90° are called right angles. Angles that measure between 90° and 180° are called obtuse angles. Angles that measure exactly 180° are called straight angles. Finally, angles that measure more than 180° but less than 360° are called reflex angles.
Another important concept in angles is the idea of complementary and supplementary angles. Two angles are complementary if their sum is equal to 90°. For example, if one angle measures 30°, then the other angle must measure 60° in order for them to be complementary. Two angles are supplementary if their sum is equal to 180°. For example, if one angle measures 120°, then the other angle must measure 60° in order for them to be supplementary.
Angles are not only important in geometry, but also in real-life applications. For example, in architecture, angles are used to design buildings and structures that are stable and aesthetically pleasing. In astronomy, angles are used to measure the position and movement of celestial objects. In physics, angles are used to calculate forces and motions of objects.
Tags:
Encyclopedia